Ultrasound Scan
Uses, Types, Procedure & Benefits
This guide is designed to explain everything about the Ultrasound test in simple, easy-to-understand English. We will cover what it is, why it’s done, how to prepare, and what to expect, so you feel confident and informed.
Summary
- What is Ultrasound?
- Why is it Safe and Preferred?
- Uses in Everyday Healthcare
What Is an Ultrasound Test?
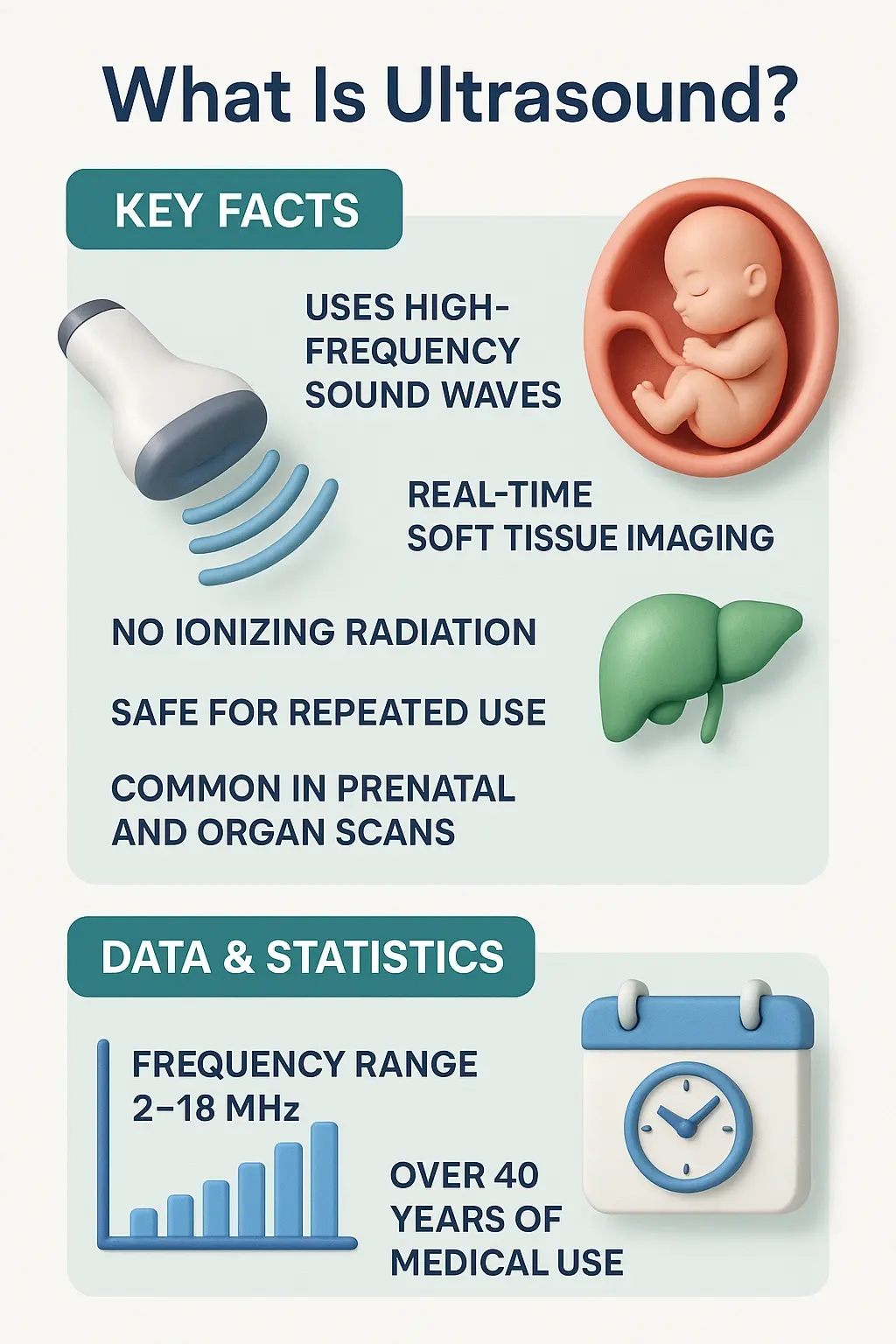
- History
- Definition and purpose of ultrasound
- How sound waves create internal images
- Key differences between ultrasound and X-ray
- Here is a simple table to show the key differences:
- Swipe right to view the full table
| Feature | Ultrasound | X-ray | MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Technology Used | High-frequency sound waves | Ionizing radiation | Magnetic fields and radio waves |
| Best For | Soft tissues, organs, blood flow, pregnancy | Bones, teeth, chest (lungs) | Detailed images of soft tissues, brain, joints |
| Safety | Very safe, no radiation | Uses a small amount of radiation | Safe, no radiation, but not for people with certain metal implants |
| Procedure | A gel is applied, and a probe is moved over the skin | You stand or lie still for a quick image capture | You lie inside a large, tube-like machine for a longer period |
Common Types of Ultrasound Scans
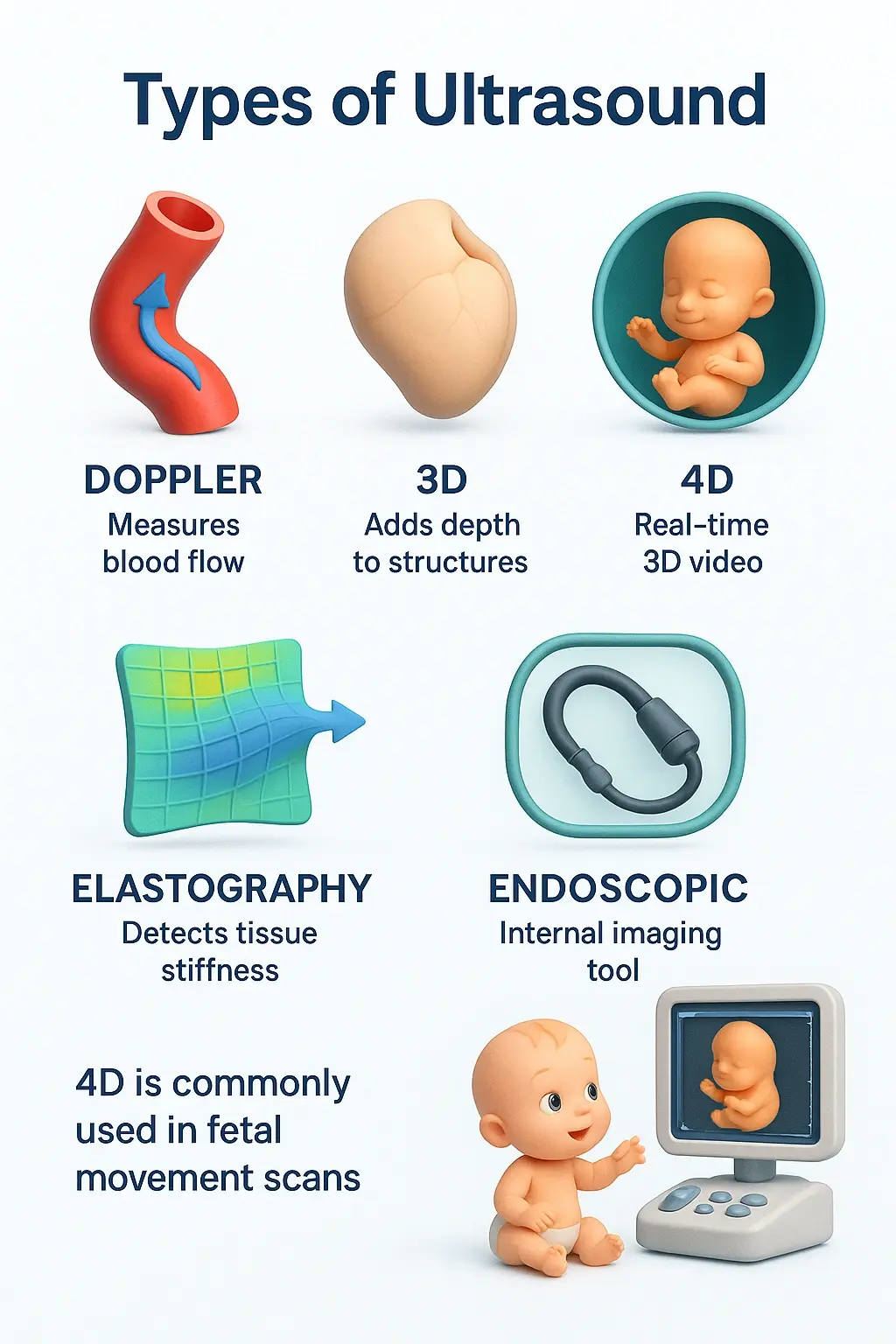
- Transvaginal and transrectal ultrasound
Why Is an Ultrasound Done?
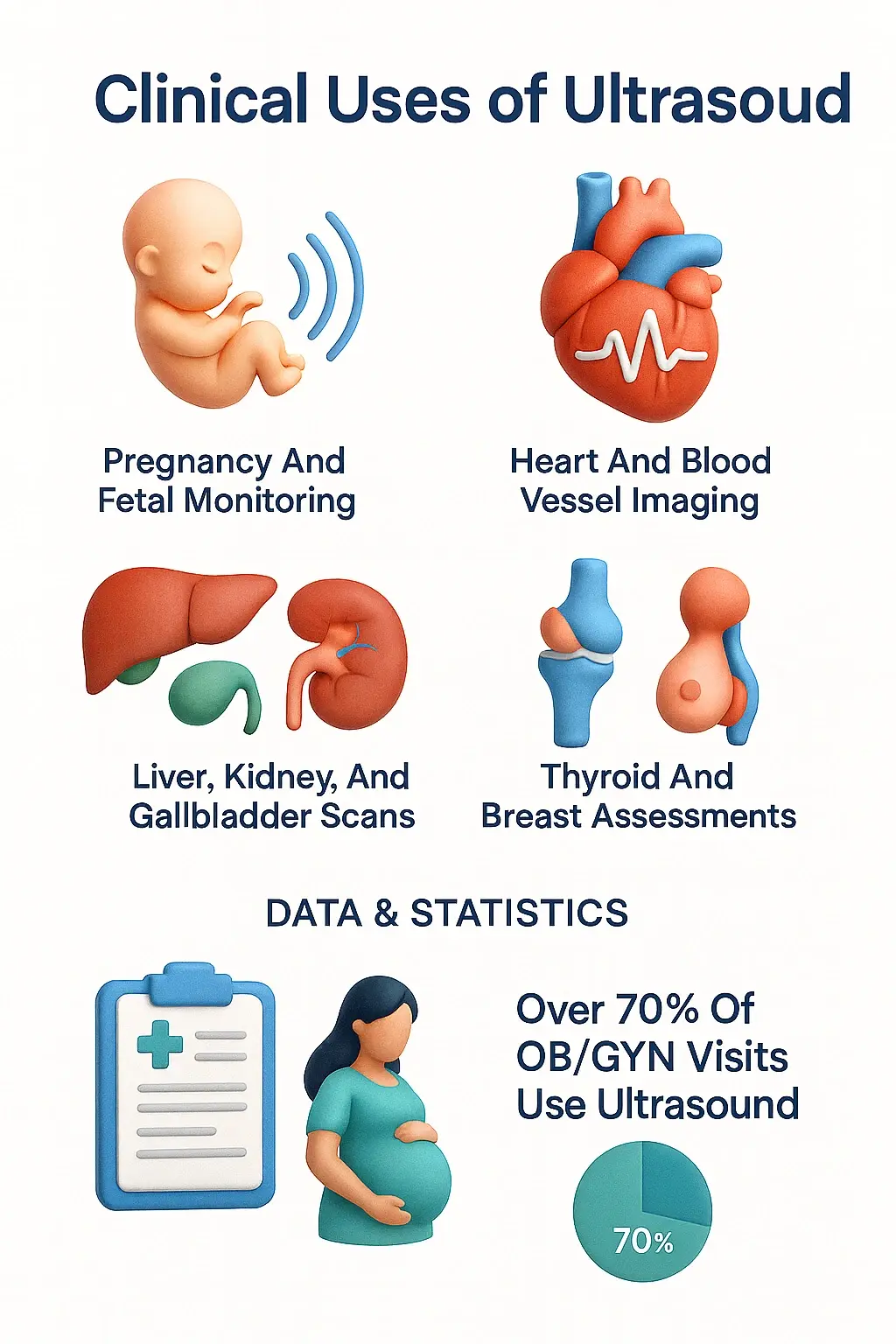
- To monitor pregnancy
- To detect internal organ problems
- To guide biopsy and needle procedures
- To evaluate symptoms like pain or swelling
Ultrasound in Pregnancy: What You Should Know
- Early pregnancy ultrasound
- Anomaly scan (level 2 scan)
- Growth scan and fetal well-being
- Gender determination laws in India
- Here is a quick overview of the key pregnancy scans:
- Swipe right to view the full table
| Scan Name (Trimester) | When It's Done | Main Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Viability Scan (First) | 6–9 weeks | To confirm pregnancy, check heartbeat, and determine the due date. |
| Nuchal Translucency (NT) Scan (First) | 11–14 weeks | To screen for chromosomal abnormalities like Down's syndrome. |
| Anomaly Scan / Level II (Second) | 18–20 weeks | A detailed check of the baby's anatomy, organs, and overall development. |
| Growth Scan (Third) | 28–36 weeks | To monitor the baby's growth, check fluid levels, and assess the placenta's health. |
Role of Ultrasound in Cancer Detection
- Ultrasound-guided biopsy and interventions
- Monitoring treatment response and recurrence
- Advantages of ultrasound in oncology

- limitations of ultrasound in oncology
How to Prepare for an Ultrasound Test
- Fasting or full bladder – when and why
⦿ Fasting: For an abdominal scan (like one for the liver or gallbladder), you may be asked not to eat or drink for 6 to 8 hours before the test. This is because food and gas in your stomach and intestines can block the sound waves and make it hard to see the organs clearly.
⦿ Full Bladder: For a pelvic or early pregnancy scan, you will be asked to drink several glasses of water an hour before your appointment and not go to the toilet. A full bladder pushes the intestines out of the way, giving the sonographer a clear view of the uterus and ovaries.
- Clothing and comfort
- Informing your doctor about medications
- This table summarises common preparation needs:
- Swipe right to view the full table
| Type of Ultrasound Scan | Preparation Required | Why It's Needed |
|---|---|---|
| Abdominal (Liver, Gallbladder) | Fast for 6–8 hours. | To reduce gas and ensure a clear view of the abdominal organs. |
| Pelvic / Early Pregnancy | Drink 4–6 glasses of water 1 hour before and hold your urine. | A full bladder provides a "window" to see the uterus and ovaries clearly. |
| Kidney | You may be asked to have a full bladder. | A full bladder helps in visualizing the kidneys and bladder more effectively. |
| Musculoskeletal / Thyroid | No special preparation needed. | These areas are close to the skin and are not affected by food or a full bladder. |
What Happens During the Procedure?
- Step-by-step ultrasound process
⦿ Check-in: You will arrive at the clinic or hospital and register for your appointment.
⦿ Preparation: A nurse or ultrasound technician will take you to the scanning room. You may be asked to change into a gown.
⦿ Positioning: You will lie down on a comfortable examination table.
⦿ Gel Application: The technician will apply a special water-based ultrasound gel to your skin over the area to be examined. This gel helps the sound waves travel from the transducer into your body.
⦿ Scanning: The technician will press the transducer firmly against your skin and move it around to capture images from different angles. You will see the black-and-white images on a computer screen.
⦿ Completion: Once enough images are captured, the technician will wipe off the gel, and you can get dressed.
- Duration and what you’ll feel
- Safety and aftercare
Ultrasound Test Results Explained
- Normal vs abnormal findings
⦿ Normal: This means that the organs look healthy and there are no signs of any problems.
⦿ Abnormal: This could mean many things, such as a cyst, a stone, inflammation, or a mass. The report might also show technical issues called ultrasound artifacts, which are not a medical problem but just distortions in the image.
- When further tests may be needed
- Interpreting reports with your doctor
Is Ultrasound Safe for Everyone?
- No radiation – major safety benefit
- Safety during pregnancy
- Myths about ultrasound side effects
Cost of Ultrasound in India
- Price range by city and type
- Ultrasound in government vs private labs
- Insurance coverage and packages
Frequently Asked Questions
Is ultrasound painful?
How long does the ultrasound scan take?
How soon are results available of ultrasound test?
Can I eat before an ultrasound?
How many ultrasounds are safe during pregnancy?
Why is an ultrasound done in pregnancy?
Can an ultrasound detect kidney stones or cancer?
What should I wear for an ultrasound scan?
Can ultrasound scans detect all medical problems?
Are there any side effects of having an ultrasound?

Written by
Dr. Harsh Shah
MS, MCh (G I cancer Surgeon)
Dr. Harsh Shah is a renowned GI and HPB Robotic Cancer Surgeon in Ahmedabad.

Reviewed by
Dr. Swati Shah
MS, DrNB (Surgical Oncology)
Dr. Swati Shah is a Robotic Uro and Gynecological Cancer Surgeon in Ahmedabad.
