Pancreatic Cancer
Causes, Symptoms & Treatment Options
The biggest challenge with this cancer is that it’s very hard to find early. It is often called a ‘silent’ disease because it usually doesn’t show any symptoms until it has already grown and spread, which makes treatment much more difficult. This is why it’s so important to understand the risk factors and recognize any possible warning signs early on.
This guide will explain the causes, symptoms, and latest treatment options for pancreatic cancer in simple terms to help you stay aware and informed.
Introduction to Pancreatic Cancer
Have a Question?
What Causes Pancreatic Cancer?
Pancreatic cancer happens when cells in the pancreas start growing out of control. Different things can raise the risk of this disease, including inherited genes, lifestyle habits, and certain health problems.

- Genetic Mutations & Family History
⦿ Inherited genetic mutations – Some people are born with gene changes that can make cells grow abnormally, leading to cancer.
⦿ Family history – If close relatives have had pancreatic cancer, there may be a higher chance of getting it.
⦿ BRCA1 & BRCA2 gene mutations – These gene changes, known for raising the risk of breast cancer and ovarian cancer, can also increase the risk of pancreatic cancer.
- Lifestyle & Environmental Risks
⦿ Smoking – Harmful chemicals in cigarettes can damage DNA and lead to cancer.
⦿ Unhealthy diet – Eating lots of processed meats and fatty foods may increase the risk.
⦿ Heavy alcohol use and pancreatitis – Drinking too much alcohol can cause long-term swelling (inflammation) in the pancreas, which can lead to cancer.
- Health Conditions That Increase Risk
⦿ Diabetes – People with long-term diabetes have a greater chance of developing pancreatic cancer.
⦿ Chronic pancreatitis – Ongoing inflammation in the pancreas can damage cells and raise the risk of cancer.
⦿ Obesity and metabolic problems – Being very overweight and having insulin-related conditions can increase the risk.
Early Signs & Symptoms of Pancreatic Cancer
- Common Symptoms
- Jaundice & Skin Changes

Dark urine and light-colored stools
- Other Warning Signs

New diabetes diagnosis in older adults
Have a Question?
How Do Doctors Diagnose Pancreatic Cancer?

- Imaging Tests & Scans
⦿ CT scan and MRI – These scans create clear images of the pancreas and nearby areas to check for cancer.
⦿ Endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) – A tiny ultrasound device is placed inside the body to get a closer look at the pancreas.
⦿ PET scan – This scan helps find cancer in other parts of the body by showing where cancer cells might be growing.
- Blood Tests & Biomarkers
⦿ CA 19-9 tumor marker test – This test looks for a special protein in the blood that may be high in people with pancreatic cancer.
⦿ Liver function tests – These tests check if the cancer is blocking the bile ducts, which can cause liver problems.
⦿ Genetic testing – This test looks for inherited gene changes that might increase the risk of pancreatic cancer.
- Biopsy & Tissue Testing
⦿ Fine-needle aspiration (FNA) biopsy – A thin needle is used to take a small piece of the pancreas for testing.
⦿ Tissue sampling – The sample is studied under a microscope to see if it has cancer cells.
⦿ Pathology testing – Doctors use this information to help decide the best treatment.
Stages of Pancreatic Cancer
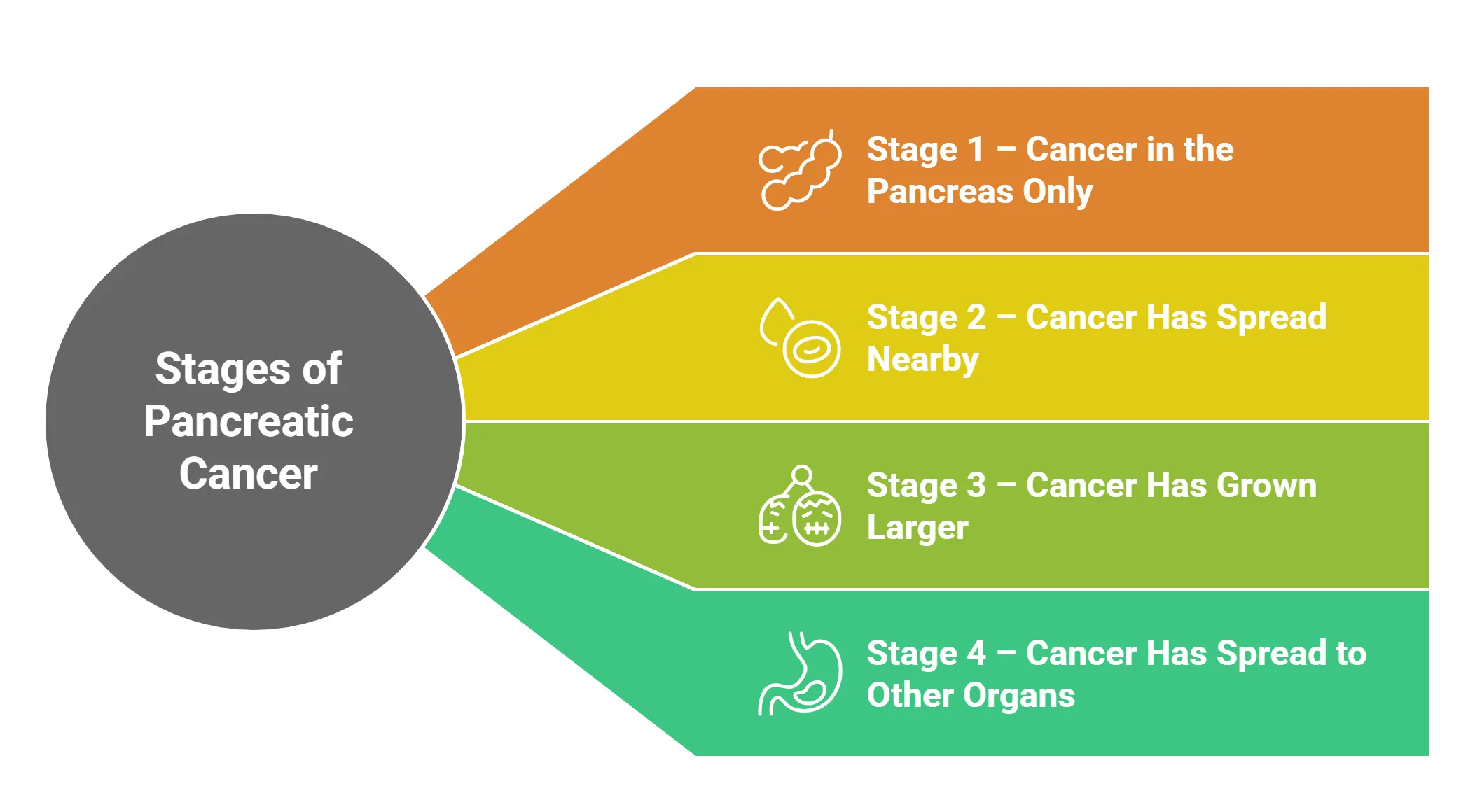
- Stage 1 – Cancer in the Pancreas Only
⦿ This is the best stage for surgery to remove it.
- Stage 2 – Cancer Has Spread Nearby
⦿ Treatment may include surgery, chemotherapy, or radiation.
- Stage 3 – Cancer Has Grown Larger
⦿ Surgery is usually not possible, and chemotherapy is the main treatment.
- Stage 4 – Cancer Has Spread to Other Organs
Treatment Options for Pancreatic Cancer
Surgery

Chemotherapy

⦿ Common chemotherapy drugs – Medicines like Gemcitabine and FOLFIRINOX help shrink tumors and slow cancer spread.
⦿ Dealing with side effects – Chemotherapy can cause nausea, tiredness, and hair loss, but doctors can help manage these symptoms.
Targeted Therapy

Radiation & Supportive Care

Radiation and other treatments can help shrink tumors and ease symptoms.
⦿ Radiation therapy – Uses high-energy rays to shrink tumors. It may be given before or after surgery.
⦿ Pain relief and support – Medications and therapies help manage pain and make the person more comfortable.
⦿ Quality of life care – For advanced cancer, palliative care focuses on comfort and symptom control.
- Therapeutic Approaches and Expected Results
- Swipe right to view the full table
| Treatment Option | Indication | Curative Potential | Survival Outcome | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Surgical Resection (Whipple / DP / TP) | Resectable disease without metastasis | Curative | 5-year survival: 20–25% (after adjuvant chemo) | Requires margin-negative resection and adjuvant therapy |
| Neoadjuvant Therapy + Surgery | Borderline resectable or locally advanced tumors | Potentially curative | Improved R0 rate and survival in selected patients | Helps downstage tumors, better selection of surgical candidates |
| Adjuvant Chemotherapy (e.g. mFOLFIRINOX) | Post-surgery in fit patients | Improves survival | Median survival: ~54 months (in PRODIGE-24 trial) | Standard after curative surgery in eligible patients |
| Systemic Chemotherapy | Metastatic or unresectable locally advanced disease | Palliative | Median survival: 8–11 months (FOLFIRINOX regimen) | FOLFIRINOX preferred in good PS; Gem/nab-paclitaxel for elderly/PS2 |
| Chemoradiation | Selected locally advanced cases | Disease control | Modest survival benefit | Use after induction chemo; not for all cases |
| Palliative Biliary Drainage / Pain Management | Advanced or unresectable disease | Symptom relief only | Varies as per stage and comorbidities | Improves quality of life |
| Supportive Care | Poor performance status, advanced stage | Symptom control only | Median survival: <6 months | Emphasis on nutrition, pain relief, and psychosocial support |
Can Pancreatic Cancer Be Prevented?
- Healthy Habits to Lower Risk
⦿ Eat nutritious foods – Include plenty of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
⦿ Stay active – Regular exercise and a healthy weight can reduce cancer risk.
⦿ Avoid smoking and heavy drinking – These can raise the risk of pancreatic cancer.

- Early Detection & Screening
⦿ Who should get genetic testing? – People with a family history of pancreatic cancer may need genetic testing.
⦿ Regular doctor visits – Checkups help spot warning signs early.
⦿ New screening methods – Advanced tools, like AI-based imaging, may help detect pancreatic cancer sooner in the future.
Importance of Awareness & Early Diagnosis
Living a healthy lifestyle, such as eating well, exercising, and getting regular checkups, can also help with prevention. New medical advancements are improving treatment options, but seeing a doctor right away if symptoms appear is key. If you or someone you know has concerns, it’s best to seek medical advice as soon as possible.
Have a Question?
Frequently Asked Questions
What is pancreatic cancer?
What are the early symptoms of pancreatic cancer?
What causes pancreatic cancer?
Who is more likely to get pancreatic cancer?
How is pancreatic cancer diagnosed?
What are the treatment options for pancreatic cancer?
Can pancreatic cancer be cured?
Does pancreatic cancer spread fast?
Can pancreatic cancer be prevented?
Is pancreatic cancer common in India?

Written by
Dr. Harsh Shah
MS, MCh (G I cancer Surgeon)
Dr. Harsh Shah is a renowned GI and HPB Robotic Cancer Surgeon in Ahmedabad.

Reviewed by
Dr. Swati Shah
MS, DrNB (Surgical Oncology)
Dr. Swati Shah is a Robotic Uro and Gynecological Cancer Surgeon in Ahmedabad.







