Kidney Cancer
Risk Factors, Prevention, and Early Detection
Often, in its early stages, kidney cancer may not show clear signs, which is why awareness of its risks and symptoms is so important. This guide will simply explain the risk factors, the symptoms to watch out for, and the latest treatment options available, helping you understand how to take the right steps for your health.
What is Kidney Cancer?
Have a Question?
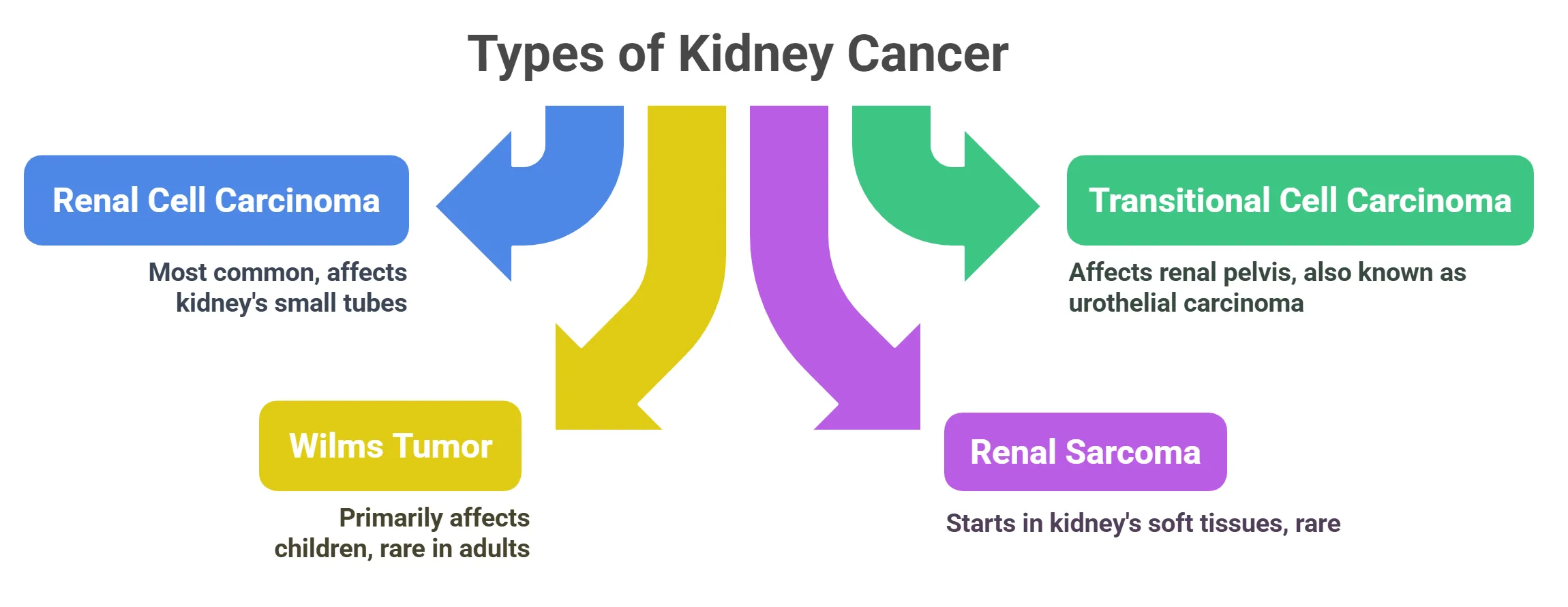
Types of Kidney Cancer
Kidney cancer starts when cells in the kidney grow out of control. There are different types of kidney cancer, depending on the kind of cells that become cancerous. Here are the main types:
⦿ Transitional Cell Carcinoma (TCC): This type of cancer starts in the renal pelvis, which is where urine collects inside the kidney. It’s also called urothelial carcinoma.
⦿ Wilms Tumor: Wilms tumor is a type of kidney cancer that usually affects children. It is rare in adults.
⦿ Renal Sarcoma: Renal sarcoma is a rare type of kidney cancer that starts in the soft tissues of the kidney.
Early Signs and Symptoms of Kidney Cancer
- Common Symptoms
Blood in Urine (Hematuria)
Persistent Pain in the Side or Back
Lump or Mass in the Side or Abdomen
- Less Common Symptoms

Fever
Swelling in Ankles and Legs
Have a Question?
Risk Factors for Kidney Cancer
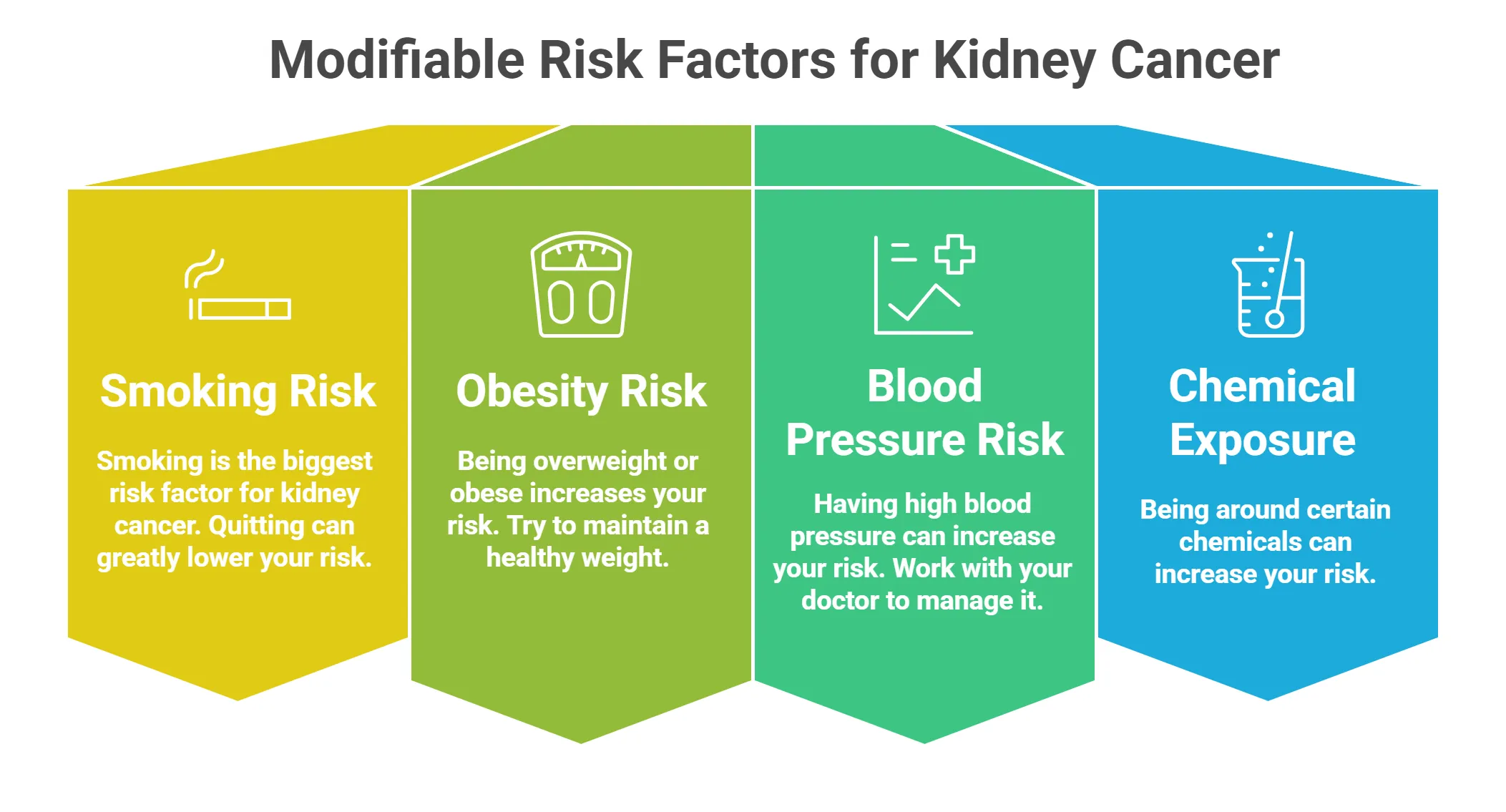
- Modifiable Risk Factors
⦿ Smoking: The Leading Cause: Smoking is the biggest risk factor for kidney cancer. If you smoke, quitting can greatly lower your risk.
⦿ Obesity: Increased Risk with Higher BMI: Being overweight or obese increases your risk. Try to maintain a healthy weight. BMI stands for Body Mass Index. Check your Body Mass Index now with BMI Calculator
⦿ High Blood Pressure (Hypertension): Having high blood pressure can increase your risk. Work with your doctor to manage your blood pressure.
⦿ Exposure to Certain Chemicals: Being around certain chemicals can increase your risk.
⦿ Asbestos, Cadmium: These chemicals are used in some jobs. If you work with them, take safety precautions.
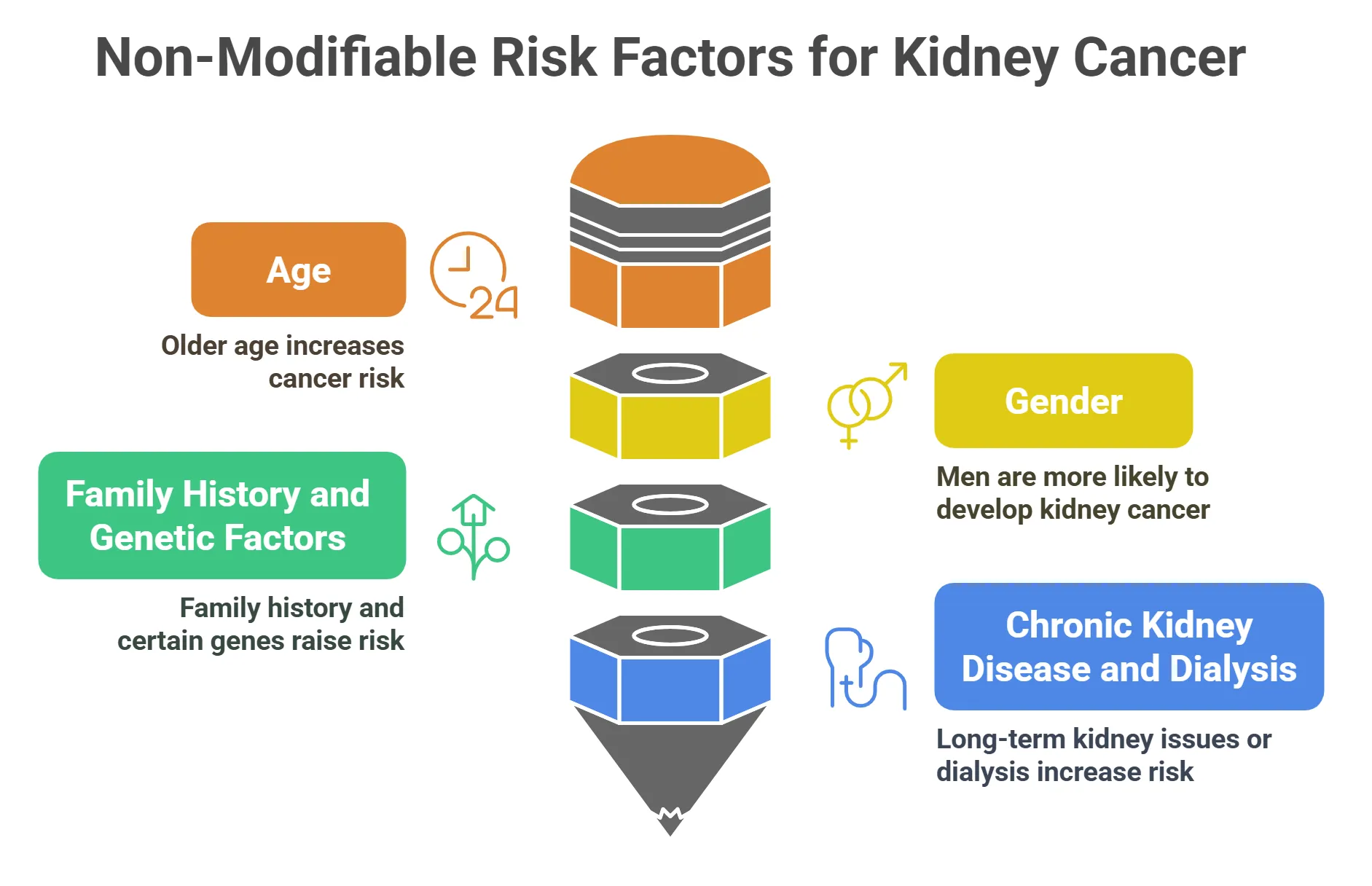
- Non-Modifiable Risk Factors
⦿ Age: The older you get, the higher your risk.
⦿ Gender: Men are more likely to get kidney cancer than women.
⦿ Family History and Genetic Factors: If you have family members who had kidney cancer, your risk might be higher. Some genes can also increase your risk.
⦿ Chronic Kidney Disease and Dialysis: Having long-term kidney problems or being on dialysis increases your risk.
How is Kidney Cancer Diagnosed?
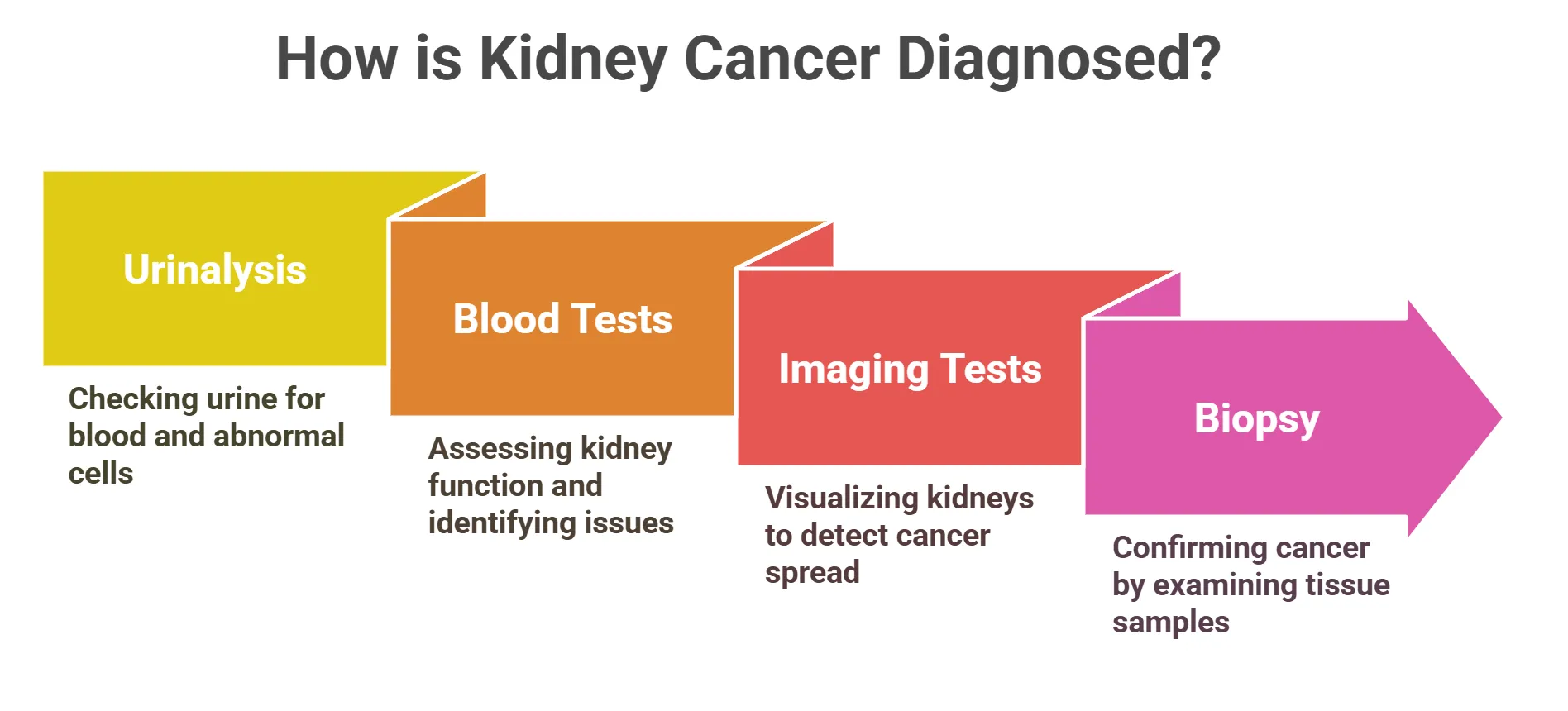

- Diagnostic Tests
⦿ Urinalysis: Checking for Blood and Abnormal Cells: Urinalysis is a test to check your pee for blood and other things. It can also find abnormal cells.
⦿ Blood Tests: Assessing Kidney Function: Blood tests can show how well your kidneys are working. They can also check for other problems.
⦿ CT scans and MRIs can show if the cancer has spread.
⦿ Ultrasounds use sound waves to create images.
⦿ Biopsy: Confirming Cancer Cells: A biopsy is when the doctor takes a small piece of tissue from your kidney. This tissue is checked under a microscope to see if there are cancer cells. A biopsy is the only way to know for sure if you have kidney cancer.
Staging of Kidney Cancer
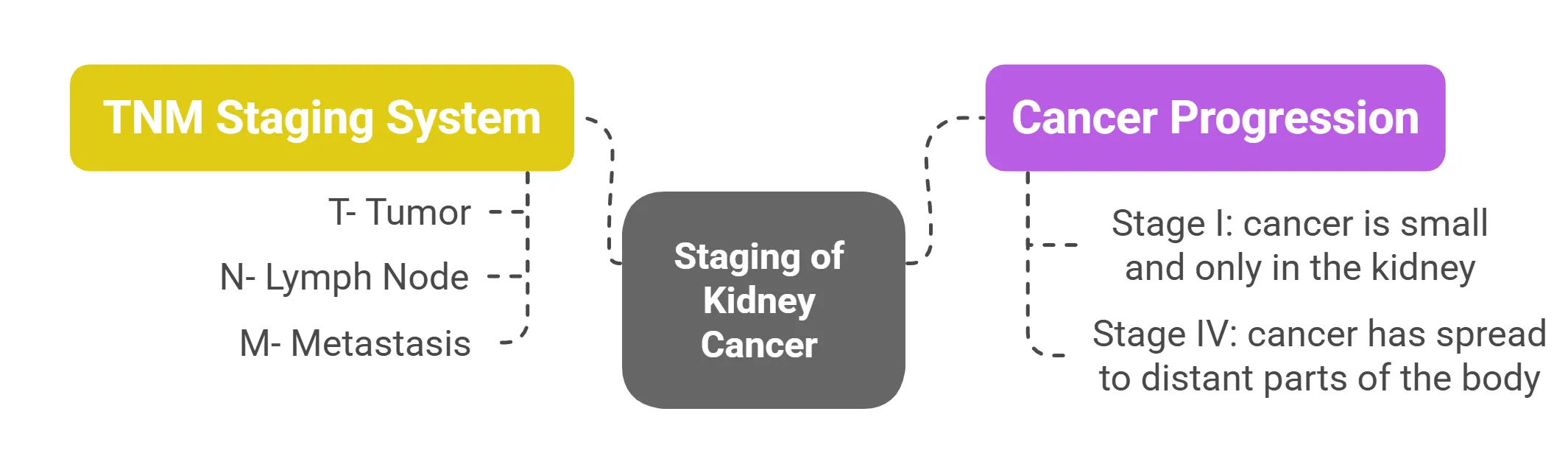
- TNM Staging System: Tumor, Node, Metastasis
⦿ N stands for whether the cancer has spread to lymph nodes.
⦿ M stands for whether the cancer has spread to other parts of the body (metastasis).
- Stages I to IV: Understanding Cancer Progression
⦿ Stage IV means the cancer has spread to distant parts of the body.
Treatment Options for Kidney Cancer
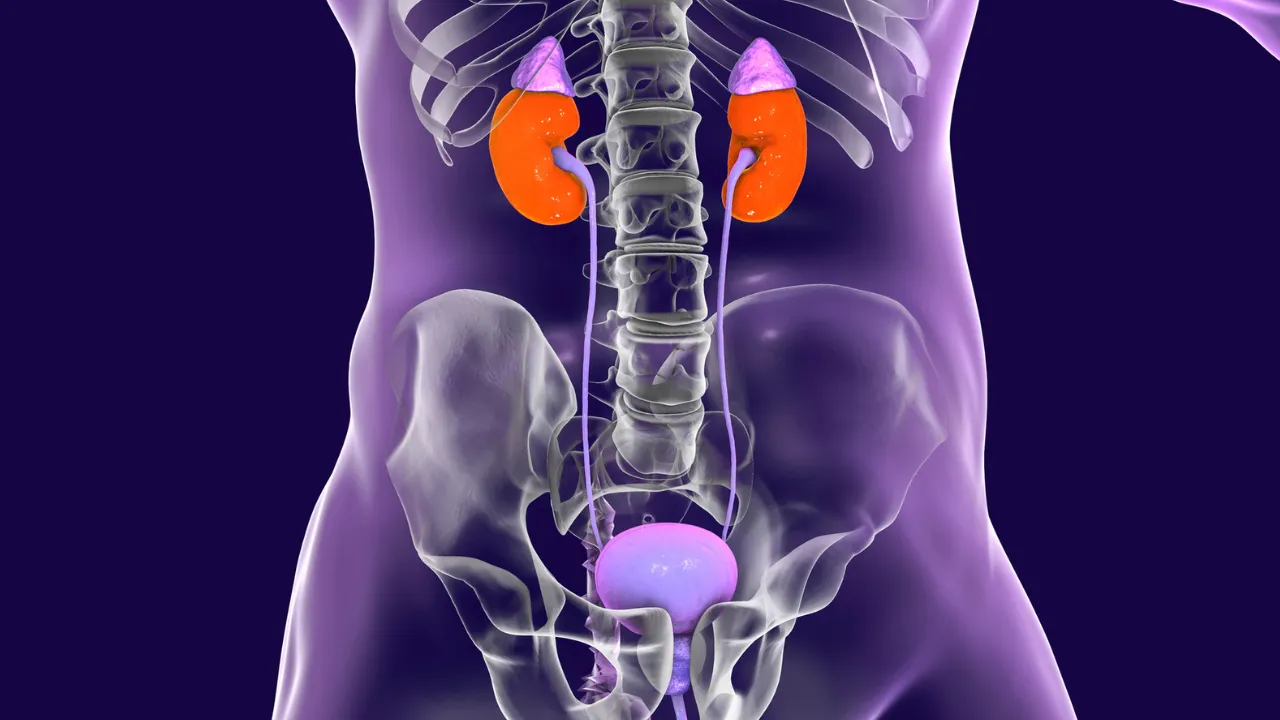
- Surgical Treatments
Radical Nephrectomy
Partial Nephrectomy
Nephroureterectomy
- Surgical Treatments
Targeted Therapy: Blocking Cancer Growth

Immunotherapy: Boosting the Immune System
Immunotherapy helps your body’s immune system fight cancer.
Radiation Therapy: External Beam Radiation

Radiation therapy uses high-energy rays to kill cancer cells. External beam radiation comes from a machine outside your body.
Ablation Techniques: Freezing or Heating Cancer Cells
Active Surveillance: Monitoring Small, Slow-Growing Tumors
Active surveillance means carefully watching the cancer with regular tests. This is done for small, slow-growing tumors.
- Stage-Based Treatment Options in Kidney Cancer
| Cancer Stage | What It Means | Treatment Options |
|---|---|---|
| Stage I | Tumor is small (≤7 cm) and limited to the kidney | - Partial or radical nephrectomy (surgery to remove part or all of the kidney) |
| Stage II | Tumor is larger (>7 cm) but still within the kidney |
- Radical nephrectomy - Regular follow-up after surgery |
| Stage III | Tumor has spread to nearby lymph nodes or major veins |
- Radical nephrectomy with lymph node removal - Targeted therapy or immunotherapy in select cases |
| Stage IV | Cancer has spread to distant organs (lungs, bones, etc.) |
- Immunotherapy - Targeted therapy - Palliative surgery if needed - Clinical trial if eligible |
Preventing Kidney Cancer
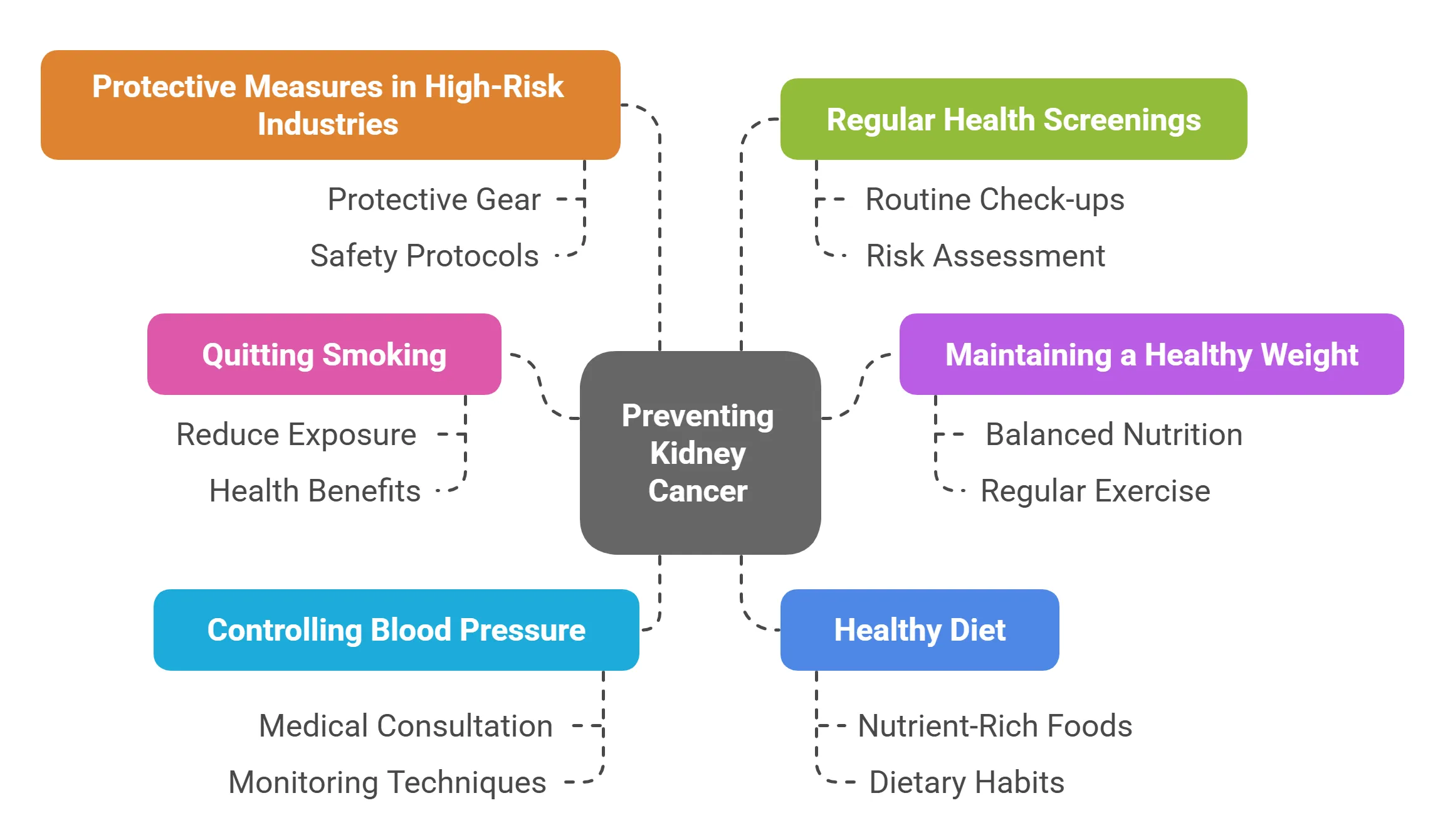
- Lifestyle Changes
⦿ Maintaining a Healthy Weight: Staying at a healthy weight can lower your risk. Try to eat healthy and exercise regularly.
⦿ Controlling Blood Pressure: Keeping your blood pressure under control can help. Work with your doctor to manage your blood pressure.
⦿ Healthy Diet: Emphasizing Fruits and Vegetables: Eating lots of fruits and vegetables can help protect against kidney cancer.
- Occupational Safety
⦿ Regular Health Screenings: If you work in a high-risk job, get regular check-ups to look for early signs of cancer.
Have a Question?
Schedule an appointment today!
Frequently Asked Questions
What is kidney cancer?
What are the common symptoms of kidney cancer?
What are the main causes and risk factors for kidney cancer?
How is kidney cancer usually diagnosed?
What are the different stages of kidney cancer?
What are the primary treatment options available for kidney cancer?
Can kidney cancer be cured, and what factors affect the chances of a cure?
What lifestyle changes can help manage or prevent kidney cancer?
What are the potential side effects of kidney cancer treatment?
Are there any new treatments or clinical trials for kidney cancer?

Written by
Dr. Swati Shah
MS, DrNB (Surgical Oncology)
Dr. Swati Shah is a Robotic Uro and Gynecological Cancer Surgeon in Ahmedabad.

Reviewed by
Dr. Harsh Shah
MS, MCh (G I cancer Surgeon)
Dr. Harsh Shah is a renowned GI and HPB Robotic Cancer Surgeon in Ahmedabad.